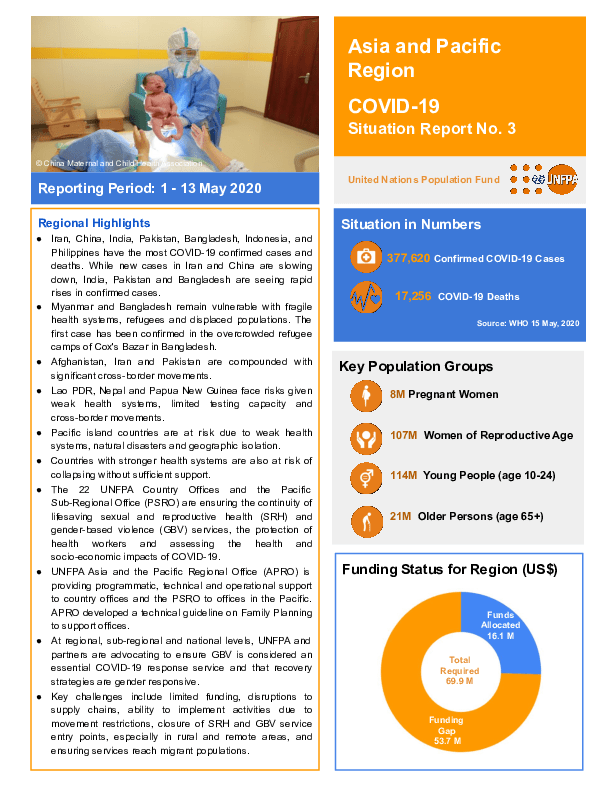
- Iran, China, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Indonesia, and Philippines have the most COVID-19 confirmed cases and deaths. While new cases in Iran and China are slowing down, India, Pakistan and Bangladesh are seeing rapid rises in confirmed cases.
- Myanmar and Bangladesh remain vulnerable with fragile health systems, refugees and displaced populations. The first case has been confirmed in the overcrowded refugee camps of Cox's Bazar in Bangladesh.
- Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan are compounded with significant cross-border movements.
- Lao PDR, Nepal and Papua New Guinea face risks given weak health systems, limited testing capacity and cross-border movements.
- Pacific island countries are at risk due to weak health systems, natural disasters and geographic isolation.
- Countries with stronger health systems are also at risk of collapsing without sufficient support.
- The 22 UNFPA Country Offices and the Pacific Sub-Regional Office (PSRO) are ensuring the continuity of lifesaving sexual and reproductive health (SRH) and gender-based violence (GBV) services, the protection of health workers and assessing the health and socio-economic impacts of COVID-19.
- UNFPA Asia and the Pacific Regional Office (APRO) is providing programmatic, technical and operational support to country offices and the PSRO to offices in the Pacific. APRO developed a technical guideline on Family Planning to support offices.
- At regional, sub-regional and national levels, UNFPA and partners are advocating to ensure GBV is considered an essential COVID-19 response service and that recovery strategies are gender responsive.
- Key challenges include limited funding, disruptions to supply chains, ability to implement activities due to movement restrictions, closure of SRH and GBV service entry points, especially in rural and remote areas, and ensuring services reach migrant populations.
Workflow State
Published
Resource Date
Show feature
No
Resource Document
Available Languages
Resource PDF Upload